Experimental Physics XI
Experimental Physics XI: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Least Count, Zero Error, Young’s Modulus of Elasticity of Material of a Metallic Wire & Specific Heat of a Liquid using Calorimeter etc.
Important Questions on Experimental Physics XI
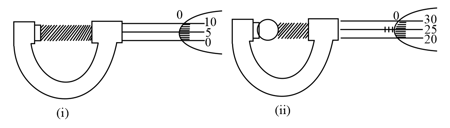
In a screw gauge, the zero of main scale coincides with fifth division of circular scale in figure (i). The circular divisions of screw gauge are It moves on main scale in one rotation. The diameter of the ball in figure (ii) is:
If division of main scale coincides with divisions of vernier scale. Given one main scale division is equal to units. Find the least count of the vernier.
The pitch of screw gauge is and its circular scale is divided into divisions. When nothing is put between the studs the zero of main scale is not seen but when circular scale is rotated by the zero of main scale is just visible and the zero of main scale coincide with the zero of circular scale. When a glass plate is placed between the studs. The circular scale lies between 18th division of main scale and circular scale reads divisions. Then,
A non-standard vernier calipers has coinciding with , with each equal to . The scale has a maximum measureable length of . If is found to coincide with where does the zero of vernier lie? Assume no zero error.
Least count of two screw gauges is same then.
A screw gauge of pitch has a circular scale divided into divisions and has no zero error. When the diameter of a wire is measured using this screw gauge, the main scale reading is and the circular division coincides with the main scale. The length of the wire is given as . The curved surface area of the wire up to the correct significant figures is
The main scale of a vernier calipers reads in millimeter and its vernier is divided into division which coincide with division of main scale. When two jaws of instrument touch each other the fourth division of the Vernier scale coincides with a main scale division and the zero of the vernier lies to the right of zero of main scale and lies
Between and division of main scale. Further more, when a cylinder is tightly placed along its length between two jaws, it is observed that division of the main scale consider sixth division of vernier scale, calculate the length of the cylinder in
A screw gauge is used to measure the thickness of thin sheet of copper. The pitch of screw gauge is and total number of division on circular scale is When two jaws are brought in contact then division of circular scale is exactly coincide with the main scale line, and that the zero of main scale is barely visible. When thickness of sheet is measured with screw gauge then main scale reading is and division coincide with the main scale line. Find the thickness of copper sheet in
The pitch of screw gauge is and there are divisions on it's circular scale. The instrument reads circular divisions when nothing is put in between it jaws. In measuring the diameter of a wire, there are divisions on the main scale and division coincides with the reference line. Then choose the correct option (s).
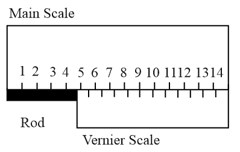
Consider the Vernier caliper as shown, the instrument has no zero error. The length of the rod (in ) shown is , if . Use . Write the value of .
The distance advanced by screw of a screw gauge is in four rotation. Its cap is divided into division. There is no zero error. If the screw reads divisions on the main scale and divisions on the cap, then the diameter of the wire is (in )-
The pitch of a screw gauge having divisions on its circular scale is . When the two jaws of the screw gauge are in contact with each other, the zero of the circular scale lies 6 division below the line of graduation. When a wire is placed between the jaws, 3 linear scale divisions (each one being ) are clearly visible while division on the circular scale coincide with the reference line. The diameter of the wire is (in ) _____.
The circular scale of a screw gauge consists of 50 divisions and the linear distance travelled by screw in one complete rotation is equal to and it is equal to the value of one pitch scale division. When nothing is placed between the studs, division of circular scale coincides with the index line of pitch scale and zero of the pitch scale is just inside the circular scale. Now a thin plate of thickness is inserted between the studs by unscrewing the circular scale and fit it just tight to measure its thickness. The minimum number of rotations to be done by the ratchet in
A spring is placed between the jaws of screw gauge such that the spring is not at all compressed. The main scale reads divisions and circular scale reads divisions. Now we turn the circular scale by such that the spring is compressed. The circular scale has divisions and the least count of the main scale is . What is the force exerted (in ) by the spring on the jaws if the spring constant is ?
The vernier of a vernier scale is divided into divisions which coincide with divisions of the main scale, each main scale division being . When the two jaws of the instrument are in contact with each other, the division of the vernier scale coincides with a main scale division and the zero of the vernier lies to the right of the zero of the main scale. When a sphere is inserted between the jaws, the zero of vernier scale lies slightly to the right of and the vernier division coincides with a main division. The diameter of sphere will be
The distance advanced by screw of a screw gauge is in four rotation. Its cap is divided into division. There is no zero error. If the screw reads divisions on the main scale and divisions on the cap, then the diameter of the wire is (in )-
End correction is a correction in :
In a vernier callipers if each centimetre of the main scale is divided into equal parts and vernier scale divisions coincide with main scale divisions, then what will be the least count?
